Lab 9 (ƒ 10) - Cranial Nerve Nuclei and Brain Stem Circulation
Blood Vessels on the Gross Specimen
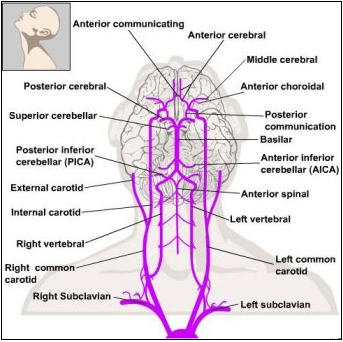
Examine the blood vessels on the anterior surface of the brainstem. Locate the vertebral arteries and posterior inferior cerebellar arteries. Trace the paired vertebral arteries that unite near the pontomedullary junction to form the basilar artery. Along its rostral course over the pons the basilar artery gives off paramedian and short and long circumferential arteries. As their name suggests, the paramedian arteries enter the brain on its anterior surface near the midline, while the short and long circumferential arteries pass around the brain stem and enter on the anterolateral or posterolateral surfaces. The anterior inferior and superior cerebellar arteries also arise from the basilar artery.
Caudal to the mammillary bodies, the basilar artery terminates as it branches into the paired posterior cerebral arteries. The oculomotor nerve passes between the branching of the superior cerebellar and posterior cerebral arteries and is vulnerable to aneurysms in either of these branches of the basilar artery. The midbrain is supplied by paramedian arteries that arise from the basilar artery (caudal midbrain) and the posterior cerebral and posterior communicating arteries (rostral midbrain) and by long and short circumferential arteries arising from both the posterior cerebral and superior cerebellar arteries.
